Home > Products > Broadband light source > SLED broadband light source > Scheme of Time-domain Optical Coherence Tomograp
Scheme of Time-domain Optical Coherence Tomograp
Time-domain optical coherence tomography (TD-OCT) is an imaging technique used to capture high-resolution cross-sectional images of biological tissues. It utilizes the principles of low-coherence interferometry to measure the depth and reflectivity of tissue structures. Scheme of Time-domain Optical Coherence Tomograp
Send Inquiry
Product Description
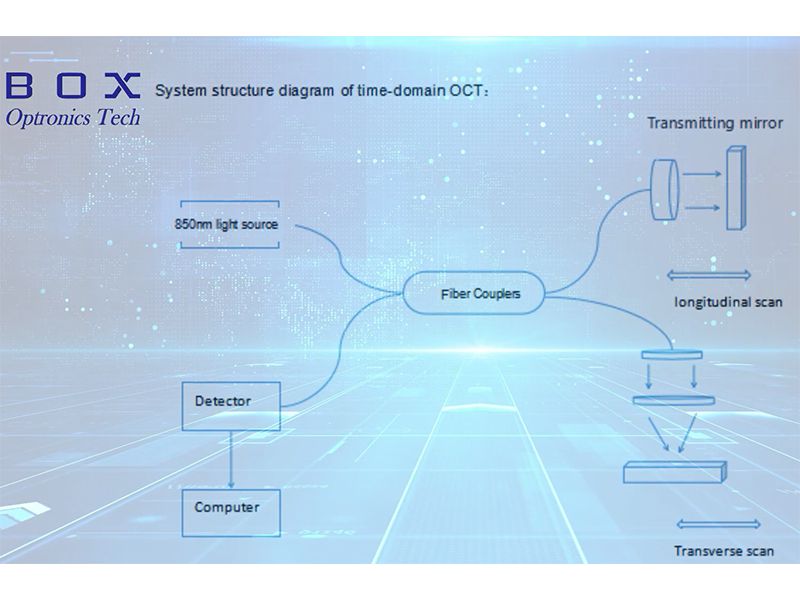
Here is a description of Scheme of Time-domain Optical Coherence Tomograp
Light Source: TD-OCT systems typically use a broadband light source, such as a superluminescent diode (SLD) or a femtosecond laser. The light source emits a broad spectrum of wavelengths, providing a high axial resolution and enabling fine details to be captured in the tissue.
Splitting the Light: The broadband light is split into two arms – the reference arm and the sample arm – using a fiber optic coupler or a beamsplitter. The reference arm contains a mirror, while the sample arm directs the light towards the tissue being imaged.
Sample Interface: The light from the sample arm is focused onto the tissue surface using a lens system or a scanning mechanism. The light interacts with the tissue, scattering and reflecting back into the system.
Interferometer: The backscattered light from the tissue and the reference light from the mirror recombine at the fiber optic coupler or beamsplitter. Interference occurs between the light waves, resulting in an interference pattern.
Detector: The interference pattern is detected by a photodetector, such as a photodiode or a spectrometer. The photodetector converts the optical signals into electrical signals.
Signal Processing: The electrical signals are processed to extract the depth information and construct the cross-sectional image of the tissue. This involves analyzing the interference pattern and performing Fourier transformations to obtain the frequency or depth domain information.
Scanning Mechanism: To capture three-dimensional images, the TD-OCT system typically employs a scanning mechanism in the sample arm. This can be a galvanometer-based scanning mirror or a rotational scanner, which allows the beam to be scanned over the tissue surface and acquire multiple cross-sectional images.
Visualization and Image Reconstruction: The processed depth information is then visualized and reconstructed into a detailed cross-sectional image of the tissue. This image provides information about tissue morphology, structure, and pathological conditions.
TD-OCT is a well-established imaging technique used in various medical and clinical applications, including ophthalmology, dermatology, cardiology, and dentistry. It offers non-invasive imaging with high resolution and depth penetration, making it valuable for diagnosing and monitoring various diseases and conditions. Ongoing research and advancements continue to enhance the performance and capabilities of TD-OCT systems, enabling further applications and improving patient care.
Light Source: TD-OCT systems typically use a broadband light source, such as a superluminescent diode (SLD) or a femtosecond laser. The light source emits a broad spectrum of wavelengths, providing a high axial resolution and enabling fine details to be captured in the tissue.
Splitting the Light: The broadband light is split into two arms – the reference arm and the sample arm – using a fiber optic coupler or a beamsplitter. The reference arm contains a mirror, while the sample arm directs the light towards the tissue being imaged.
Sample Interface: The light from the sample arm is focused onto the tissue surface using a lens system or a scanning mechanism. The light interacts with the tissue, scattering and reflecting back into the system.
Interferometer: The backscattered light from the tissue and the reference light from the mirror recombine at the fiber optic coupler or beamsplitter. Interference occurs between the light waves, resulting in an interference pattern.
Detector: The interference pattern is detected by a photodetector, such as a photodiode or a spectrometer. The photodetector converts the optical signals into electrical signals.
Signal Processing: The electrical signals are processed to extract the depth information and construct the cross-sectional image of the tissue. This involves analyzing the interference pattern and performing Fourier transformations to obtain the frequency or depth domain information.
Scanning Mechanism: To capture three-dimensional images, the TD-OCT system typically employs a scanning mechanism in the sample arm. This can be a galvanometer-based scanning mirror or a rotational scanner, which allows the beam to be scanned over the tissue surface and acquire multiple cross-sectional images.
Visualization and Image Reconstruction: The processed depth information is then visualized and reconstructed into a detailed cross-sectional image of the tissue. This image provides information about tissue morphology, structure, and pathological conditions.
TD-OCT is a well-established imaging technique used in various medical and clinical applications, including ophthalmology, dermatology, cardiology, and dentistry. It offers non-invasive imaging with high resolution and depth penetration, making it valuable for diagnosing and monitoring various diseases and conditions. Ongoing research and advancements continue to enhance the performance and capabilities of TD-OCT systems, enabling further applications and improving patient care.
Hot Tags: Scheme of Time-domain Optical Coherence Tomograp, China, Manufacturers, Suppliers, Factory, Customized, Cheap, Low Price, Brands, Quotation, Price
Related Category
Send Inquiry
Please Feel free to give your inquiry in the form below. We will reply you in 24 hours.